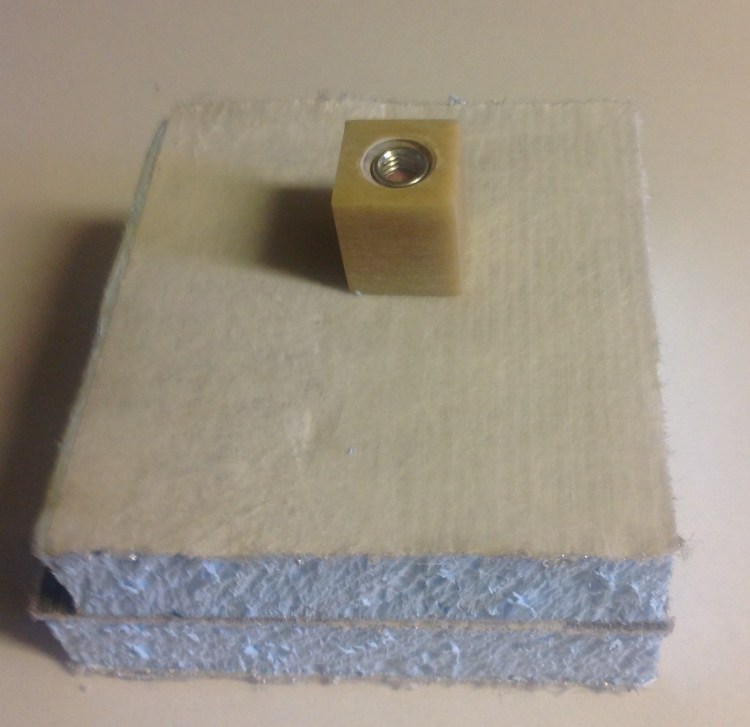
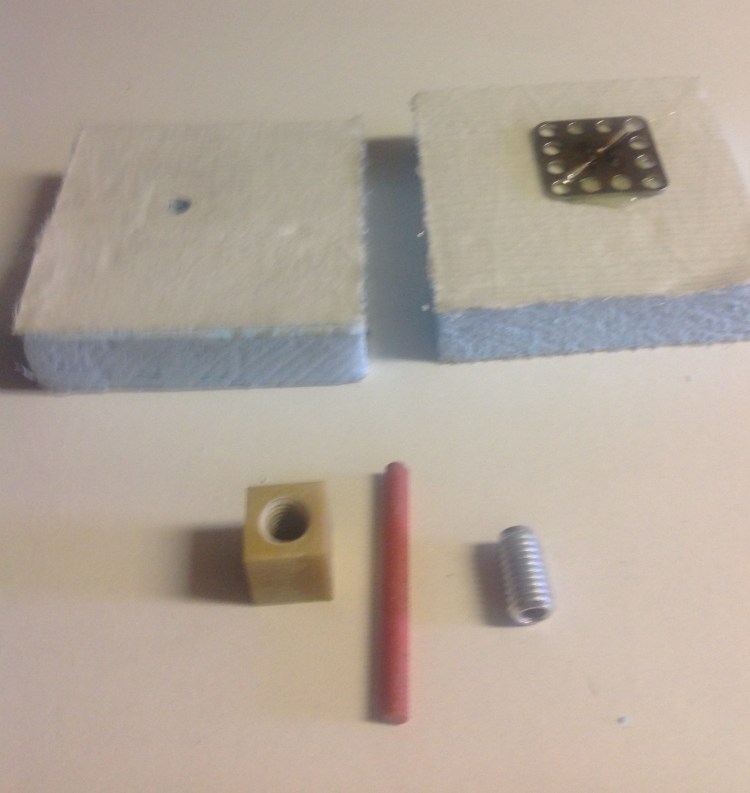
The differential thread connector, application as tension nut
The clamping movement of a tension nut is axial (along the longitudinal axis of the connection), the clamping effect is obtained without rotating of the nut.
Clamping without rotation friction between the nut and the fixing surface is characterised by a favourable and predictable torch-tension ratio, independent of the nature of the fixing surface. The fixing surface or washer is better protected against damage. The nut may have an asymmetric shape and can be positioned before it is clamped.
This application of the differential thread connector is demonstrated below.
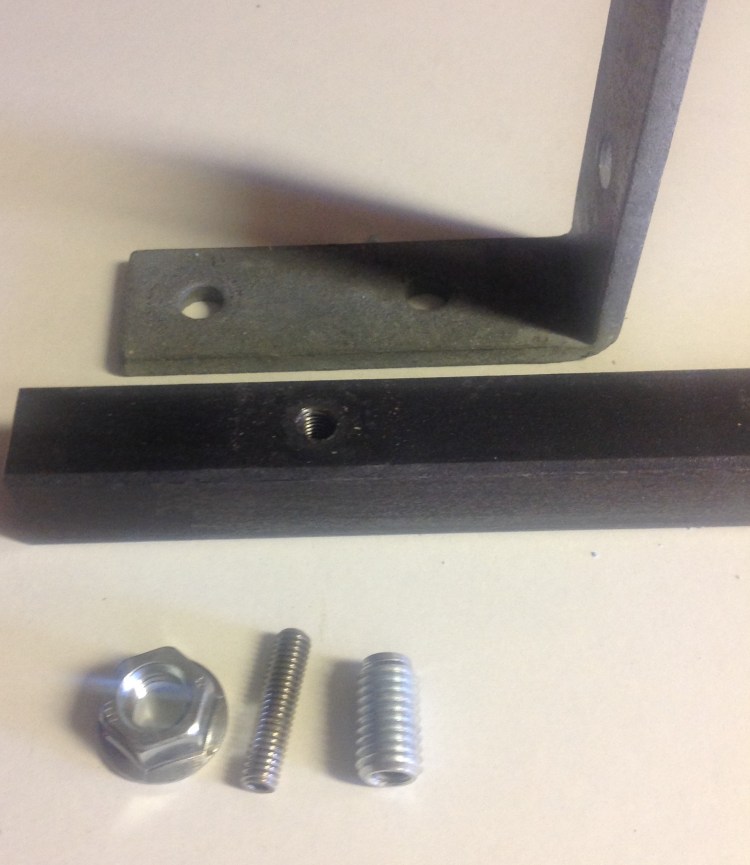
The connector is installed inside a 10M nut and turned on a M6 bolt fixed in a threaded fixing point (tapped or as insert). When the nut/connector is close to the fixing surface, the rotation movement is stopped and the connector is turned counter clockwise. Thereby the desired clamping effect is obtained.
Examples:
- Sandwich panels clamped together between a BigHead fixing point and a FRP M10 nut with connector inside.
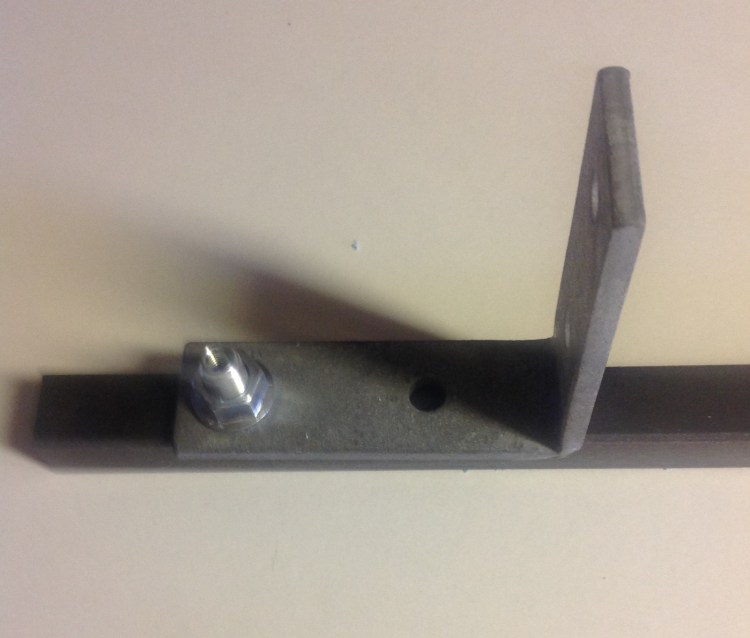
B. Metal fitting clamped to a steel beam between a serrated flange nut (M10) with connector inside, and a tapped fixing point in the steel beam